一、原理介绍
1.什么是频率计
频率计是一种专门对被测信号频率进行测量的电子测量仪器。本实验是基于FPGA的频率计,所以主要用于测量方波,若需要测其他波形,则需要加入前级信号处理电路。
2.测量方法与基本原理
1)FPGA普通测量法
直接计数单位时间内的脉冲数。在1s闸门时间内,记录被测信号的脉冲个数Nx,则待测频率Fx=Nx,此方法对低频信号测量误差较大,舍弃。
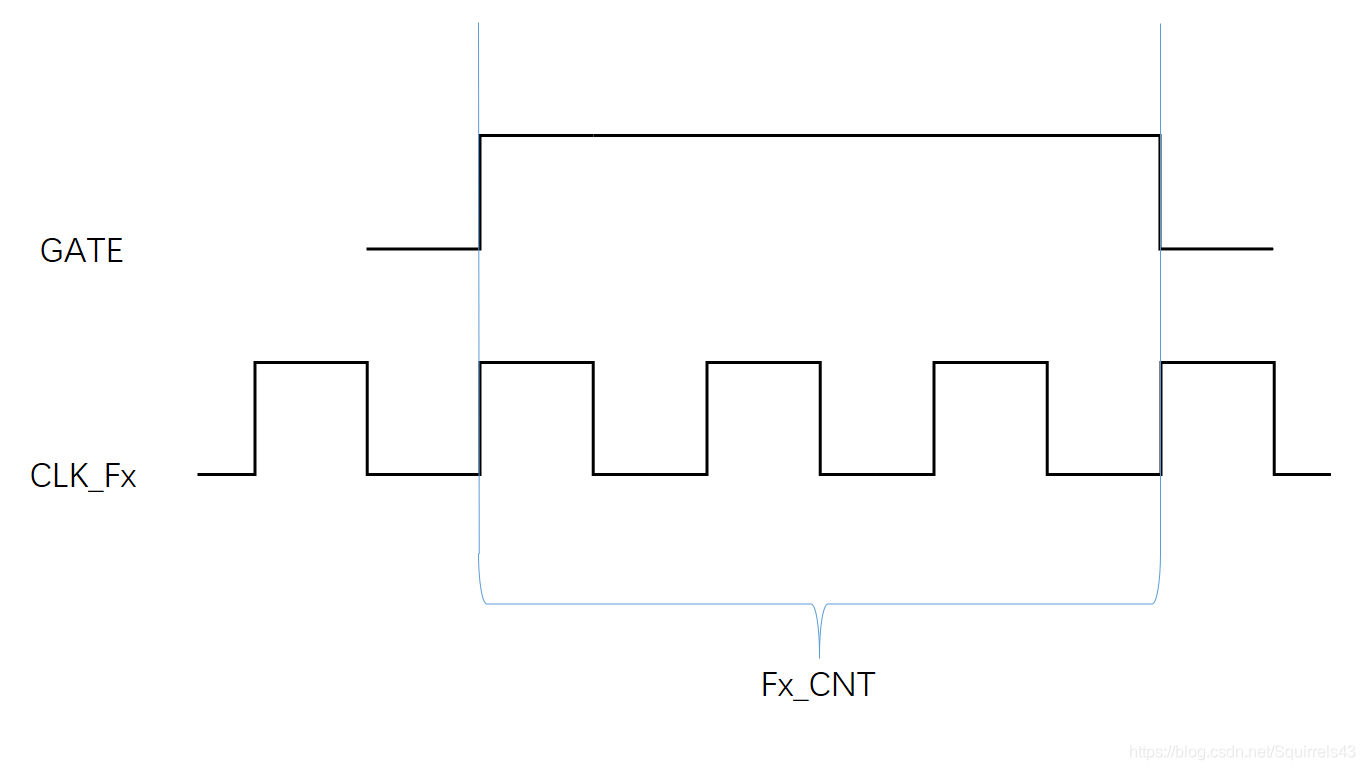
普通测量法(图未画基准时钟)
测量时,门宽不一定为1s,所以给出通常情况下的计算公式:
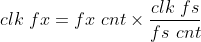
其中,clk_fs为基准时钟,clk_fx为待测信号,fs_cnt为基准时钟个数,fx_cnt为待测时钟个数
2)FPGA等精度测量法
本方案除给定闸门时间外,还由被测信号再生成一路计数允许信号。计数允许信号在闸门时间内第一个被测信号的上升沿开启,在闸门时间结束后被测信号的第一个上升沿结束,最后在计数允许信号的有效时间内,分别对标准频率信号个数、被测信号个数和被测信号高电平时间内标准频率信号个数计数后,再经过相关运算即可得所求频率、占空比和时间间隔。
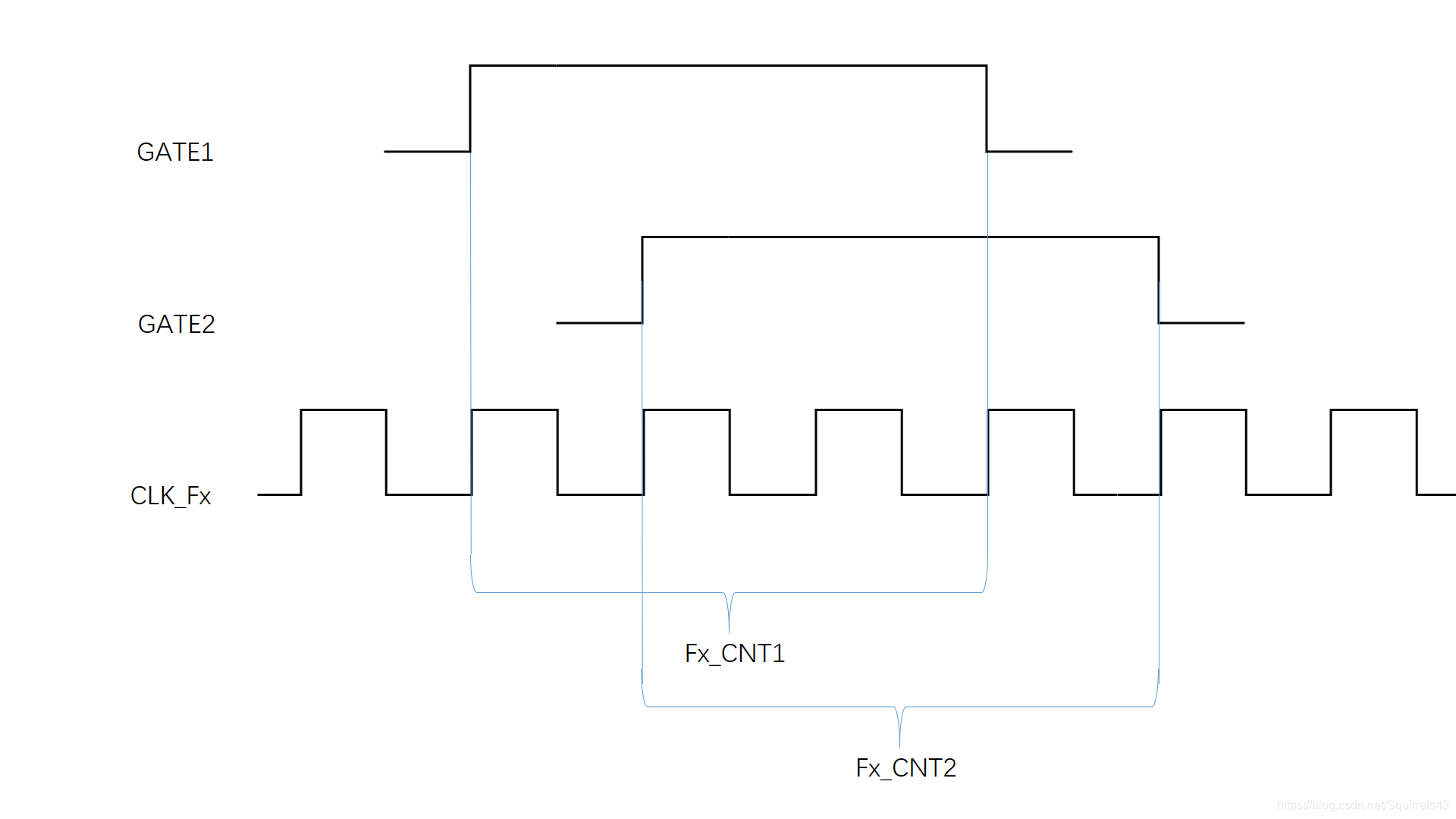
等精度测量法(同样未画基准时钟)
3)FPGA代码设计
FPGA主要完成测量待测信号频率,对输入信号个数和标准信号个数进行计数。本实验针对这部分进行设计。
3.待测信号如何输入FPGA
1)管脚图:GPIO部分(FPGA型号:Cyclone III EP3C16F484C6N)
FPGA主要完成测量待测信号频率,对输入信号个数和标准信号个数进行计数。本实验针对这部分进行设计。
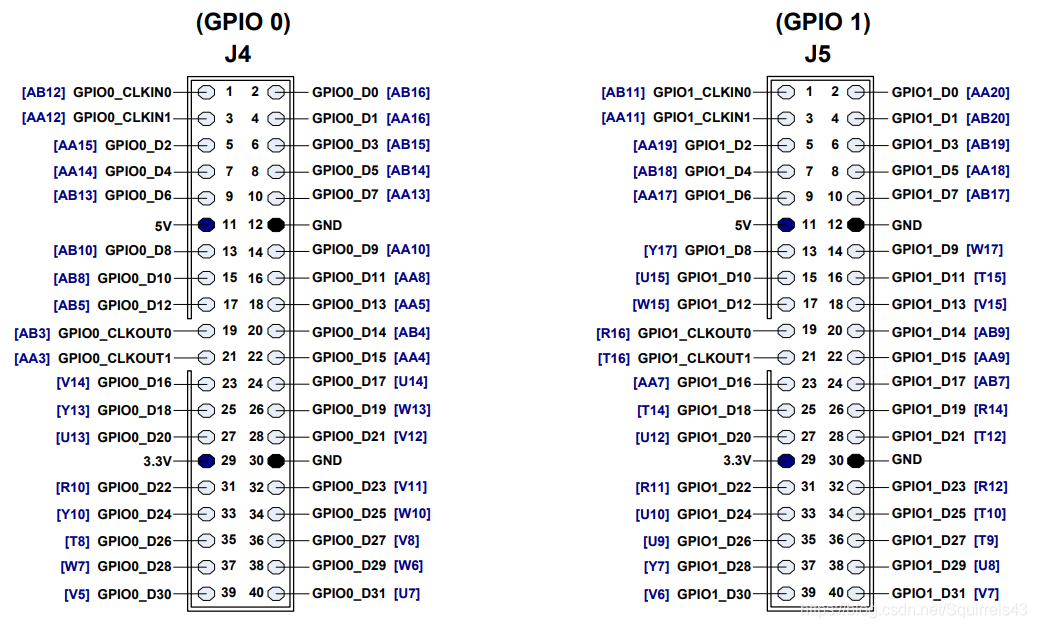
原则:一定!一定!一定注意所配管脚与实际管脚的位置,配哪个用哪个,用哪个配哪个。
2)使用杜邦线连接信号源,为防止FPGA被烧坏,信号源要设置为输出3.3Vpp,偏移1.65V。
二、实验程序
1.RTL图
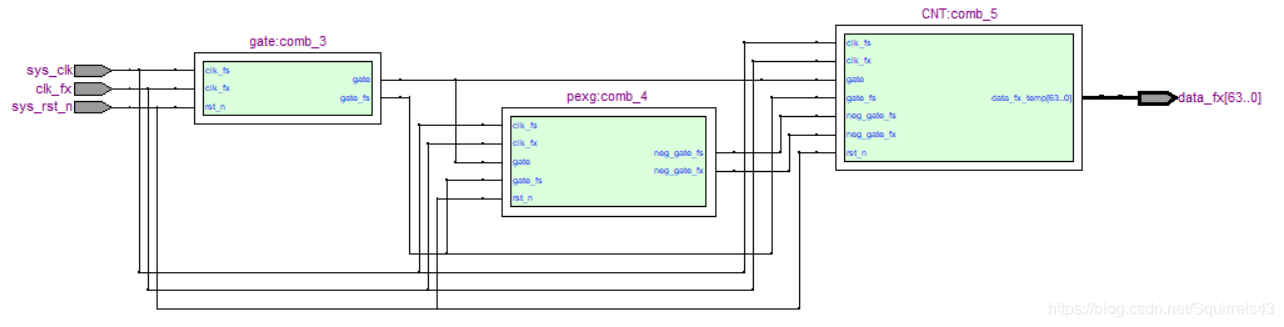
显而易见,频率计有三个部分:门信号,边沿检测,计数器
2.Verilog(参考设计)
1.门控部分:
module gate
(
input clk_fs , // 基准时钟信号
input rst_n , // 复位信号
//cymometer interface
input clk_fx ,//待测信号
output reg gate , //门控信号
output reg gate_fs // 同步到基准时钟的门控信号
);
localparam GATE_TIME = 16'd5_000; // 门控时间设置
reg [15:0] gate_cnt ; // 门控计数
reg gate_fs_r ; // 用于同步gate信号的寄存器
//门控信号计数器,使用被测时钟计数
always @(posedge clk_fx or negedge rst_n) begin
if(!rst_n)
gate_cnt <= 16'd0;
else if(gate_cnt == GATE_TIME + 5'd20)
gate_cnt <= 16'd0;
else
gate_cnt <= gate_cnt + 1'b1;
end
//门控信号,拉高时间为GATE_TIME个实测时钟周期
always @(posedge clk_fx or negedge rst_n) begin
if(!rst_n)
gate <= 1'b0;
else if(gate_cnt < 4'd10)
gate <= 1'b0;
else if(gate_cnt < GATE_TIME + 4'd10)
gate <= 1'b1;
else if(gate_cnt <= GATE_TIME + 5'd20)
gate <= 1'b0;
else
gate <= 1'b0;
end
//将门控信号同步到基准时钟下
always @(posedge clk_fs or negedge rst_n) begin
if(!rst_n) begin
gate_fs_r <= 1'b0;
gate_fs <= 1'b0;
end
else begin
gate_fs_r <= gate;
gate_fs <= gate_fs_r;
end
end
endmodule2.边沿检测
module pexg(
input clk_fs , // 基准时钟信号
input rst_n , // 复位信号
input clk_fx ,
input gate,
input gate_fs ,
output neg_gate_fs,
output neg_gate_fx
);
reg gate_fs_d0 ; // 用于采集基准时钟下gate下降沿
reg gate_fs_d1 ; //
reg gate_fx_d0 ; // 用于采集被测时钟下gate下降沿
reg gate_fx_d1 ; //
//wire define
//边沿检测,捕获信号下降沿
assign neg_gate_fs = gate_fs_d1 & (~gate_fs_d0);
assign neg_gate_fx = gate_fx_d1 & (~gate_fx_d0);
//打拍采门控信号的下降沿(被测时钟)
always @(posedge clk_fx or negedge rst_n) begin
if(!rst_n) begin
gate_fx_d0 <= 1'b0;
gate_fx_d1 <= 1'b0;
end
else begin
gate_fx_d0 <= gate;
gate_fx_d1 <= gate_fx_d0;
end
end
//打拍采门控信号的下降沿(基准时钟)
always @(posedge clk_fs or negedge rst_n) begin
if(!rst_n) begin
gate_fs_d0 <= 1'b0;
gate_fs_d1 <= 1'b0;
end
else begin
gate_fs_d0 <= gate_fs;
gate_fs_d1 <= gate_fs_d0;
end
end
endmodule3.计数器
module CNT
#(parameter CLK_FS = 26'd50_000_000,// 基准时钟频率
parameter MAX = 10'd64) // 定义数据位宽
( //system clock
input clk_fs , // 时钟信号
input rst_n , // 复位信号
//cymometer interface
input clk_fx , // 待测信号
input gate, // 门控信号(与待测时钟同步)
input gate_fs, // 与基准时钟同步的门控信号
input neg_gate_fx,//
input neg_gate_fs,//
output reg [MAX-1:0] fs_cnt , //门控时间内基准时钟信号的个数
output reg [MAX-1:0] fx_cnt , // 门控时间内待测信号的个数
output reg [MAX-1:0] data_fx_temp // 待测信号的频率值
);
reg [MAX-1:0] fs_cnt_temp ; // fs_cnt 计数
reg [MAX-1:0] fx_cnt_temp ; // fx_cnt 计数
//门控时间内待测信号的计数,设置的为5000个,这里重新计数,只是用于检验信号是否正确
always @(posedge clk_fx or negedge rst_n) begin
if(!rst_n) begin
fx_cnt_temp <= 32'd0;
fx_cnt <= 32'd0;
end
else if(gate)begin
fx_cnt_temp <= fx_cnt_temp + 1'b1;
end
else if(neg_gate_fx) begin
fx_cnt_temp <= 32'd0;
fx_cnt <= fx_cnt_temp;
end
end
//门控时间内基准时钟的计数
always @(posedge clk_fs or negedge rst_n) begin
if(!rst_n) begin
fs_cnt_temp <= 32'd0;
fs_cnt <= 32'd0;
end
else if(gate_fs)
begin
fs_cnt_temp <= fs_cnt_temp + 1'b1;
end
else if(neg_gate_fs) begin
fs_cnt_temp <= 32'd0;
fs_cnt <= fs_cnt_temp;
end
end
//计算待测信号的频率值
always @(posedge clk_fs or negedge rst_n) begin
if(!rst_n) begin
data_fx_temp <= 64'd0;
end
else if(gate_fs == 1'b0)
data_fx_temp <=CLK_FS*fx_cnt/fs_cnt;
end
endmodule4.顶层
module top_cymometer(
//system clock
input sys_clk , // 时钟信号
input sys_rst_n, // 复位信号
//spi没有使用
// input CS_N,
// input SCLK,
// output MISO,
//cymometer interface
input clk_fx , // 被测时钟
// output clk_out , // 输出时钟
// output [7:0] led0,
// output [7:0] led1,
// output [7:0] led2,
// output [7:0] led3,
output [63:0]data_fx
);
//parameter define
parameter CLK_FS = 26'd50000000; // 基准时钟频率值
gate//生成门控信号
(
.clk_fs (sys_clk ), // 基准时钟信号
.rst_n (sys_rst_n), // 复位信号
//cymometer interface
.clk_fx (clk_fx ), //待测信号
.gate(gate ) , //门控信号
.gate_fs(gate_fs) // 同步到基准时钟的门控信号
);
pexg//边沿捕获
(
.clk_fs (sys_clk ), // 基准时钟信号
.rst_n (sys_rst_n), // 复位信号
.gate(gate ) , //门控信号
.gate_fs(gate_fs), // 同步到基准时钟的门控信号
.clk_fx (clk_fx), //待测信号
.neg_gate_fs(neg_gate_fs),
.neg_gate_fx(neg_gate_fx)
);
CNT
(
//system clock
.clk_fs (sys_clk ), // 基准时钟信号
.rst_n (sys_rst_n), // 复位信号
//cymometer interface
.clk_fx (clk_fx ), //待测信号
.gate(gate ) ,//门控信号
.gate_fs(gate_fs) ,// 同步到基准时钟的门控信号
.neg_gate_fs(neg_gate_fs),
.neg_gate_fx(neg_gate_fx),
.fs_cnt(fs_cnt) , // 门控时间内基准时钟的计数值
.fx_cnt(fx_cnt) , // 门控时间内被测时钟的计数值
.data_fx_temp(data_fx)
);
//通过SPI模块实现与单片机通信
//spi(.clk(sys_clk),
// .rst_n(sys_rst_n),
// .CS_N(CS_N),
// .SCLK(SCLK),
// .MOSI(MOSI),
// .txd_data(data_fx),
// .MISO (MISO)
// );
//实现比较,最后调试是通过signaltap分析
//seg_led u_seg_led(
// //module clock
// .clk (sys_clk ), // 数码管驱动模块的驱动时钟
// .rst_n (sys_rst_n), // 复位信号
//user interface
// .data (data_fx ), // 被测频率值
// .seg_led0 (led0),
// .seg_led1 (led1),
// .seg_led2 (led2),
// .seg_led3 (led3)
//);
endmodule3.指派引脚(很坑)
原则:就是上述原则,用哪个配哪个,要看清楚
to, location
# 50 MHz clock input
sys_clk , PIN_G21
sys_rst_n , PIN_G3
clk_fx , PIN_AB11由于输出使用SignalTap查看,所以就不指派输出的引脚了,关于SignalTap文件的设置:
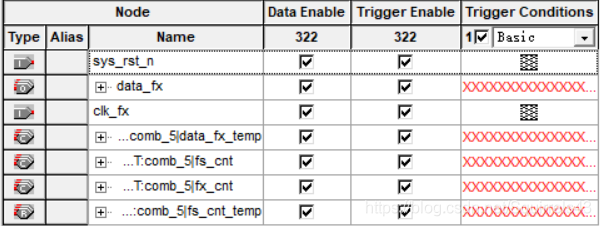
sys_clk为50MHz系统时钟,stp主要是为了查看data_fx信号,其他的不重要。
二、调试验证
1.输入不同频率的方波
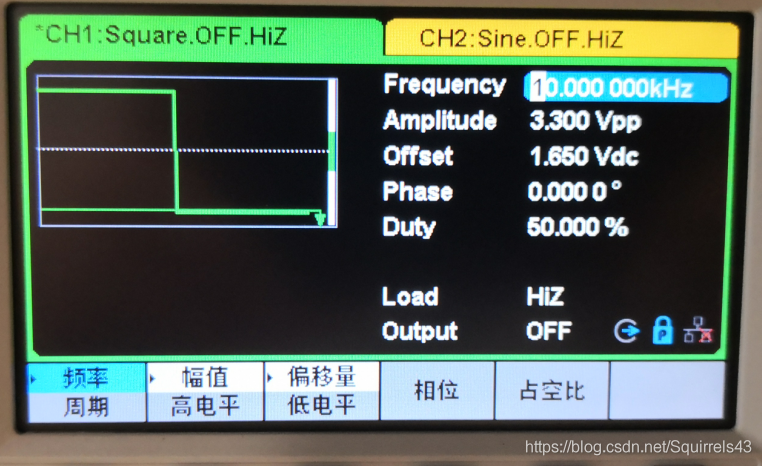
信号源调整为如图,原则为上述原则,后续只需要更改频率,频率过低的话,测试太慢,从2k开始
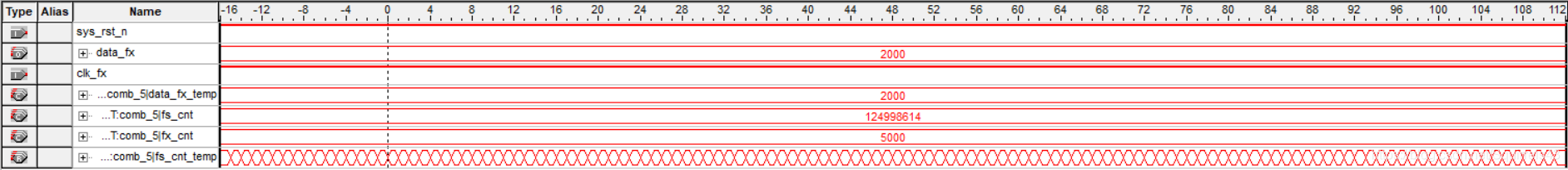
2kHz:
100kHz:

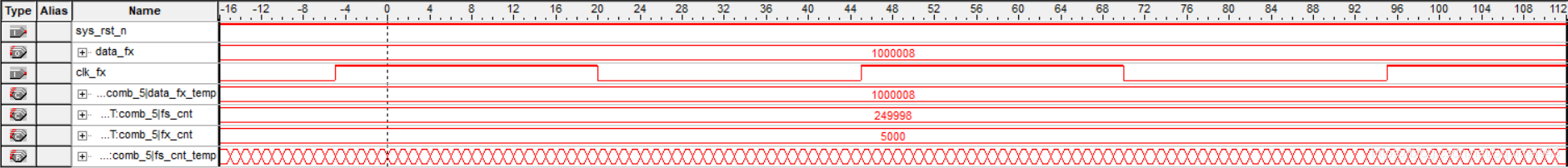
1MHz:
10MHz:

7355608Hz:
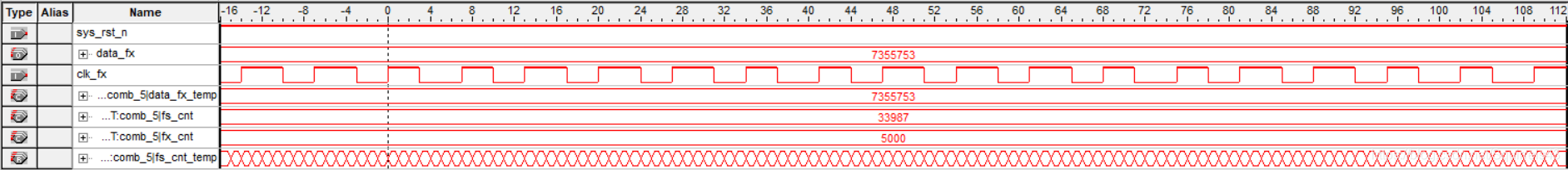
频率为1k的整数倍时,测量结果精确,频率非整数时,信号源输出可能会有问题,导致一定的误差。
OVER结束